Toyota Yaris: Fuel Sender Gauge Assembly / Inspection
INSPECTION
PROCEDURE
1. INSPECT FUEL SENDER GAUGE ASSEMBLY
CAUTION:
Perform the inspection in a well-ventilated area.
Do not perform the inspection near an open flame.
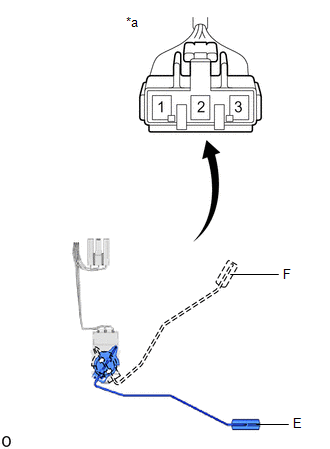
(a) Check that the float moves smoothly between F and E.
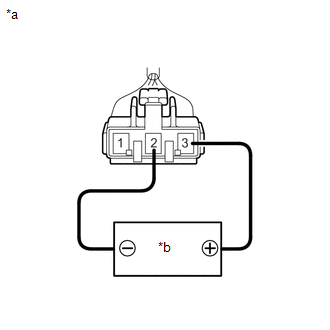
(b) Check the fuel sender gauge assembly voltage.
| (1) Apply 5 V between terminals 2 and 3. NOTICE:
HINT: If a stable power supply is not available, connect 4 nickel-metal hydride batteries (1.2 V each) or equivalent in series. |
|
| (2) Measure the voltage according to the value(s) in the table below. Standard Voltage:
*: The output voltage changes depending on the voltage applied to the terminals. Output voltage (F) = (0.851 x Voltage applied to terminals) to (0.921 x Voltage applied to terminals) Output voltage (E) = (0.069 x Voltage applied to terminals) to (0.139 x Voltage applied to terminals) If the result is not as specified, replace the fuel sender gauge assembly. |
|
2. INSPECT NO. 2 FUEL SENDER GAUGE ASSEMBLY
CAUTION:
Perform the inspection in a well-ventilated area.
Do not perform the inspection near an open flame.
(a) Check that the float moves smoothly between F and E.
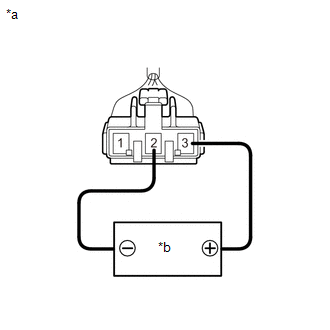
(b) Check the No. 2 fuel sender gauge assembly voltage.
| (1) Apply 5 V between terminals 2 and 3. NOTICE:
HINT: If a stable power supply is not available, connect 4 nickel-metal hydride batteries (1.2 V each) or equivalent in series. |
|
| (2) Measure the voltage according to the value(s) in the table below. Standard Voltage:
*: The output voltage changes depending on the voltage applied to the terminals. Output voltage (F) = (0.851 x Voltage applied to terminals) to (0.921 x Voltage applied to terminals) Output voltage (E) = (0.069 x Voltage applied to terminals) to (0.139 x Voltage applied to terminals) If the result is not as specified, replace the No. 2 fuel sender gauge assembly. |
|
 Removal
Removal
REMOVAL CAUTION / NOTICE / HINT CAUTION:
Never perform work on fuel system components near any possible ignition sources.
Vaporized fuel could ignite, resulting in a serious accident...
 Installation
Installation
INSTALLATION PROCEDURE 1. INSTALL NO. 2 FUEL SENDER GAUGE ASSEMBLY (a) Attach the claw and install the No. 2 fuel sender gauge assembly. NOTICE: Be careful not to bend the arm of the fuel sender gauge assembly...
Other information:
Toyota Yaris XP210 (2020-2026) Reapir and Service Manual: Freeze Frame Data
FREEZE FRAME DATA DESCRIPTION The ECM records vehicle and driving condition information as Freeze Frame Data the moment a DTC is stored. When troubleshooting, Freeze Frame Data can be helpful in determining whether the vehicle was moving or stationary, whether the engine was warmed up or not, whether the air fuel ratio was lean or rich, as well as other data recorded at the time of a malfunction...
Toyota Yaris XP210 (2020-2026) Reapir and Service Manual: Propeller Shaft System
Problem Symptoms TablePROBLEM SYMPTOMS TABLE HINT: Use the table below to help determine the cause of problem symptoms. If multiple suspected areas are listed, the potential causes of the symptoms are listed in order of probability in the "Suspected Area" column of the table...
Categories
- Manuals Home
- Toyota Yaris Owners Manual
- Toyota Yaris Service Manual
- Removal
- Fuse Panel Description
- Maintenance
- New on site
- Most important about car
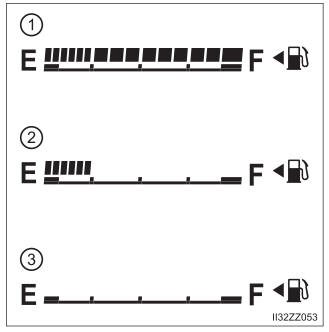
Fuel Gauge
The fuel gauge shows approximately how much fuel is remaining in the tank when the ignition is switched ON. We recommend keeping the tank over 1/4 full.